Understanding the Gearing Ratio
Introduction
The gearing ratio is a crucial financial metric used to assess a company’s financial leverage and long-term solvency. It helps investors, analysts, and business owners understand how much of a company’s capital structure is funded by debt relative to equity. A high gearing ratio indicates higher reliance on debt, which can increase financial risk, while a low gearing ratio suggests greater financial stability.
This article explores the importance of gearing ratios, their calculation methods, advantages, disadvantages, and practical applications in financial decision-making.
What is the Gearing Ratio?
The gearing ratio measures the proportion of a company’s debt relative to its equity or total capital. It is used to evaluate a company’s ability to meet its financial obligations and assess its overall financial risk.
The gearing ratio is often expressed as a percentage and can be calculated using different formulas, depending on the specific financial metric being analyzed.
Common Gearing Ratio Formulas
1. Debt-to-Equity Ratio (D/E Ratio)
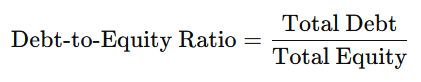
- A ratio above 1 indicates that the company has more debt than equity.
- A ratio below 1 suggests that the company relies more on equity financing.
2. Debt Ratio
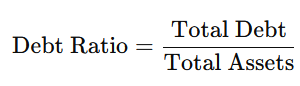
- This ratio shows how much of a company’s assets are financed through debt.
3. Equity Ratio
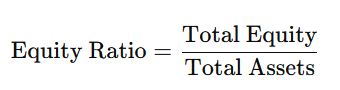
- A higher equity ratio signifies lower financial risk and greater financial stability.
4. Interest Coverage Ratio
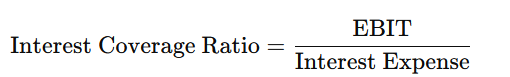
- Measures how easily a company can pay its interest obligations using its earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
- A low interest coverage ratio indicates potential difficulties in meeting interest payments.
Importance of the Gearing Ratio
- Assessing Financial Stability – Helps determine whether a company has a sustainable debt structure.
- Evaluating Risk Exposure – Companies with high gearing ratios are more exposed to financial risk in economic downturns.
- Investment Decision-Making – Investors use the gearing ratio to assess the risk-reward balance before investing in a company.
- Creditworthiness & Loan Approval – Lenders consider gearing ratios before providing loans to companies.
- Strategic Financial Planning – Companies use the gearing ratio to decide whether to raise funds through debt or equity.
High vs. Low Gearing Ratio
| Factor | High Gearing Ratio | Low Gearing Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Level | High financial risk | Lower financial risk |
| Debt Dependence | High reliance on borrowed funds | Mostly equity-funded |
| Interest Burden | Higher interest payments | Lower interest obligations |
| Potential for Growth | Higher potential returns (if debt is used effectively) | Slower but stable growth |
| Investor Perception | Risky but potentially profitable | Stable and less risky |
Factors Affecting the Gearing Ratio
- Industry Standards – Some industries (e.g., utilities and real estate) naturally operate with high gearing ratios.
- Economic Conditions – In recession periods, companies with high debt levels face more financial stress.
- Company Growth Stage – Startups and growing firms may have high gearing ratios due to aggressive expansion plans.
- Interest Rates – Rising interest rates increase the cost of debt and impact gearing levels.
- Management Decisions – Some companies strategically maintain a high gearing ratio to maximize growth opportunities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gearing
Advantages
✔ Tax Benefits – Interest payments on debt are tax-deductible.
✔ Leverage for Growth – Companies can expand operations using borrowed capital.
✔ Retains Ownership – Unlike issuing equity, taking on debt does not dilute ownership.
Disadvantages
✘ Higher Financial Risk – Increased debt leads to greater interest obligations and repayment pressures.
✘ Reduced Creditworthiness – High gearing ratios can make it harder to secure additional financing.
✘ Vulnerability to Economic Downturns – Companies with high debt struggle during recessions.
How Companies Manage Gearing Levels
To maintain an optimal gearing ratio, companies use strategies such as:
- Debt Restructuring – Refinancing existing debt with better interest rates.
- Issuing Equity – Raising capital by selling shares to reduce reliance on debt.
- Increasing Revenue & Profitability – Boosting earnings to improve financial ratios.
- Cost-Cutting Measures – Reducing operational expenses to enhance financial stability.
- Diversifying Funding Sources – Using a mix of long-term and short-term debt.
Conclusion
The gearing ratio is a key financial indicator that measures a company’s financial risk and long-term sustainability. While debt can be beneficial for growth, excessive reliance on borrowing increases risk. Balancing debt and equity financing is crucial for financial stability and long-term success.
Investors, analysts, and business owners should regularly monitor the gearing ratio to make informed financial decisions and ensure the company’s financial health remains strong.
Read this: Tariffs: Definition, Types, Impact & Global Implications