Understanding Human Reproduction
Introduction
Human reproduction is a fundamental biological process that ensures the continuation of our species. It involves complex systems within the male and female bodies, working in harmony to create new life. Understanding these systems is crucial for sexual health, family planning, and overall well-being.
The Male Reproductive System
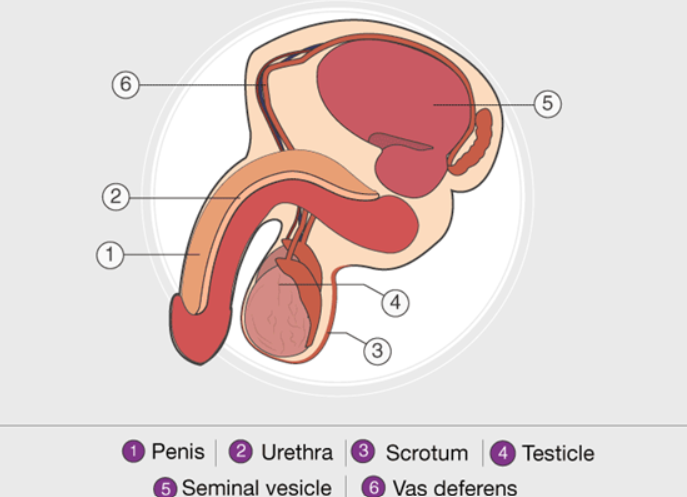
The male reproductive system is responsible for producing, storing, and delivering sperm, the male gamete necessary for fertilization.
Key Organs and Functions
- Testes (Testicles):
- Primary reproductive organs that produce sperm and testosterone.
- Sperm production occurs in the seminiferous tubules.
- Epididymis:
- A coiled tube where sperm mature and are stored before ejaculation.
- Vas Deferens:
- Transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation.
- Seminal Vesicles and Prostate Gland:
- Produce fluids that nourish and protect sperm, forming semen.
- Penis:
- Facilitates the delivery of sperm into the female reproductive tract.
Sperm Production Process (Spermatogenesis)
- Occurs continuously throughout a man’s life after puberty.
- Typically, millions of sperm are produced daily, but only a few hundred successfully reach the egg during fertilization.
The Female Reproductive System
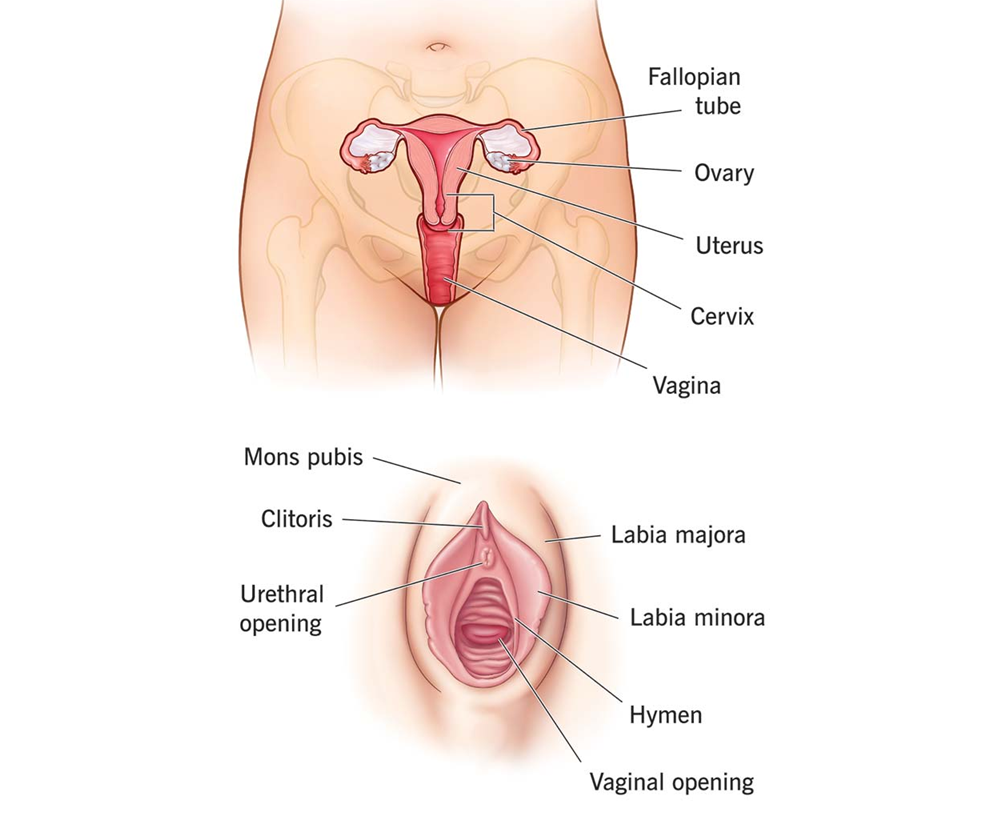
The female reproductive system is designed to produce eggs (ova), facilitate fertilization, and support the development of a fetus during pregnancy.
Key Organs and Functions
- Ovaries:
- Produce eggs and secrete hormones such as estrogen and progesterone.
- Fallopian Tubes:
- Transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Fertilization typically occurs here.
- Uterus (Womb):
- A muscular organ where the fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus.
- Cervix:
- Connects the uterus to the vagina, acting as a protective barrier.
- Vagina:
- Serves as the passageway for sexual intercourse and childbirth.
Egg Production Process (Oogenesis)
- Females are born with a finite number of eggs (approximately 1-2 million).
- Only a few hundred eggs will mature and be released during ovulation across a woman’s reproductive years.
The Process of Conception
Conception occurs when a sperm cell successfully fertilizes an egg, resulting in the formation of a zygote.
Steps of Conception
- Ovulation:
- An egg is released from one of the ovaries into the fallopian tube.
- Fertilization:
- Sperm must swim through the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes to reach the egg.
- The sperm penetrates the egg’s outer layer, and their genetic material combines to form a zygote.
- Implantation:
- The zygote travels to the uterus, where it embeds itself in the uterine lining.
- Embryonic Development:
- The zygote rapidly multiplies and develops into an embryo, eventually forming a fetus.
Pregnancy and Fetal Development
Pregnancy is a nine-month journey marked by crucial developmental milestones.
Stages of Pregnancy
- First Trimester (0-12 weeks):
- Major organs and body systems begin to develop.
- The heart starts beating by the fifth week.
- Second Trimester (13-26 weeks):
- Facial features, limbs, and internal organs mature.
- The baby begins to move, and the mother can feel the movements.
- Third Trimester (27-40 weeks):
- The baby gains weight rapidly, and the lungs mature.
- By week 37, the fetus is considered full-term.
Importance of Prenatal Care
- Regular prenatal check-ups ensure the mother and baby are healthy.
- Key tests include ultrasound scans, blood tests, and nutritional assessments.
Common Misconceptions about Reproduction
- “You can’t get pregnant the first time you have sex.”
- Pregnancy is possible any time sperm meets an egg, regardless of sexual history.
- “Withdrawal method is highly effective.”
- This method has a high failure rate due to pre-ejaculate containing sperm.
- “Sperm die immediately outside the body.”
- Sperm can survive for several minutes to hours depending on environmental conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding human reproduction empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their sexual health.
- Both the male and female reproductive systems play essential roles in conception and pregnancy.
- Safe sexual practices, contraceptive methods, and prenatal care are crucial for maintaining reproductive well-being.
Conclusion
Human reproduction is a remarkable process involving intricate biological systems working together. By gaining deeper insights into these mechanisms, individuals can better understand their bodies, make informed health decisions, and ensure a safe and responsible approach to sexual activity and family planning.
Read This: Maintaining Hygiene in Intimacy: Essential Practices for Sexual Health
Read This: Understanding Lubricants: Types and Uses for Intimacy
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on sexual health.