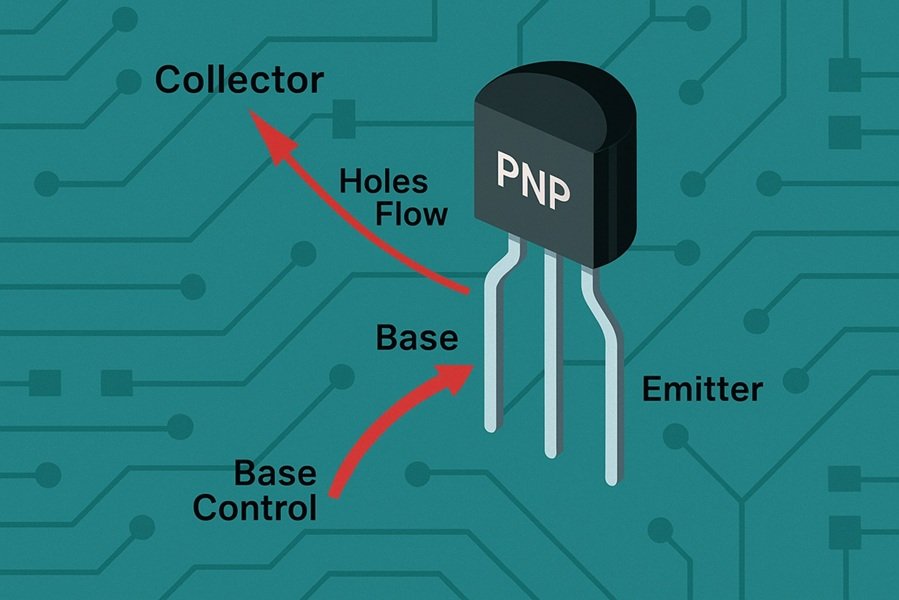
What Are PNP Transistors
What are PNP Transistors?
A PNP transistor is a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) where the majority charge carriers are holes (positive charge). It is constructed with three layers of semiconductor material: P-type, N-type, and P-type again, hence the name PNP.
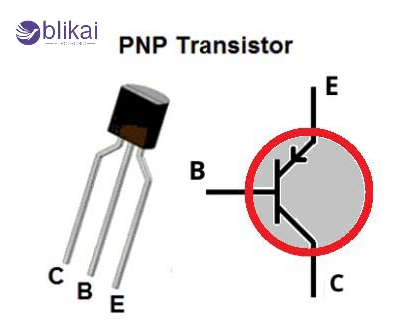
Applications of PNP Transistors
Amplification circuits
PNP transistors are key devices in amplification circuits, particularly in audio applications. They are mainly used to increase the various amplified signals that produce high sound through the preamplifiers of microphones and amplifiers for electric guitars. This PNP transistor takes advantage of its characteristics to reproduce a high-quality sound virtually distortion-freely.
Switching applications
PNP transistors excel in switching applications. They are commonly used in logic circuits and digital systems where rapid on-off switching is required. PNP transistors can effectively control larger currents with smaller input signals, making them valuable in relay drivers and motor control circuits.
Current sources
PNP transistors are excellent for creating stable current sources. This capability is instrumental in analog circuits where consistent current flow is crucial. Applications include LED drivers, where PNP transistors can maintain a steady current to ensure uniform brightness across multiple LEDs.
Level shifting
In mixed-voltage systems, PNP transistors are invaluable for level shifting. They can translate signals between different voltage levels, allowing communication between components operating at various voltages. This function is essential in modern electronic designs with standard power rails.
Selecting the Right PNP Transistor
Key parameters to consider
Some parameters must be considered when selecting the proper PNP transistor for any application. To start, think about the maximum collector current IC and maximum collector-emitter voltage VCEO ratings to determine the transistor’s power handling capacity. The current gain hF is also very significant because it informs us how many times the transistor can amplify the base current. Consider switching speed, which is essential for high-frequency applications, as shown by rise and fall time parameters.
Common PNP transistor models
Common PNP Transistor Models-Several popular PNP transistor models are used in many types of electronic circuits. 2N3906 is a general-purpose small-signal transistor that finds use in low-power applications. For higher power requirements, the TIP32 series is commonly employed. The BC557 is another versatile option for small-signal amplification and switching applications. These models offer different specifications and are chosen based on the specific needs of the circuit design.
Reading datasheets effectively
One should learn how to read datasheets effectively to make an informed decision when choosing a PNP transistor. The most outstanding indicators are those absolute maximum ratings that show the transistor will meet the requirements of your circuit. With extreme attention, look at the electrical characteristics table containing typical and maximum values for the different parameters. The graphs and charts in the datasheet are valuable because they provide a good overview of how the transistor works in various conditions. By recognizing these features, this information will allow you to select the most appropriate PNP transistor for your application.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying short circuits
A short circuit with PNP transistors could damage the device and affect the circuit’s operation. You can test for short normally using a multimeter by taking either continuity testing mode or resistance mode. Test between the collector and emitter terminals. A reading of zero or very low resistance indicates a short circuit. Also, check between the base and emitter and base and collector. Any unexpected low resistance readings between these terminals suggest a short circuit.
Detecting open circuits
An open circuit occurs if there is an interruption in the internal connections of the transistor. Set your multimeter to the diode test mode to detect an open circuit. Place the red probe on the base and the black probe on the emitter. You should see a forward voltage drop (typically 0.6-0.7V). Repeat this test with the red probe on the base and the black probe on the collector. You likely have an open circuit if either test shows no reading or “OL” (overload).
Addressing leakage problems
Leakage problems in PNP transistors may cause unwanted current flow, affecting the circuit’s performance. For leakage testing, use a multimeter with the highest resistance setting. Connect the positive lead to the emitter and harmful to the collector. A suitable PNP transistor should show very high resistance or “OL.” If you get a lower resistance reading, it indicates leakage—similarly, test between the base-collector and base-emitter. Any unexpected low resistance readings in these tests suggest leakage issues that need addressing.
Conclusion
Testing PNP transistors is a life-bearing test that every electronics enthusiast and professional should have. Good testing not only aids in identifying faulty components but also ensures the reliability of electronic projects. Testing PNP transistors, whether for basic trouble-fixing or advanced refining techniques, surely elevates one’s expertise level in electronics.