Purchasing Power Parity (PPP): A Detailed Analysis
Introduction
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) is an economic theory that compares the purchasing power of different countries’ currencies through a common basket of goods and services. It provides a more accurate measure of economic well-being by adjusting exchange rates to reflect the actual cost of living in different nations. PPP is widely used by economists, policymakers, and international organizations like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to compare economic productivity and living standards across countries.
What is Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)?
Definition:
PPP is a method of measuring the relative value of currencies by comparing the price of identical goods and services in different countries. The concept is based on the idea that in the absence of transportation costs and trade barriers, identical goods should have the same price when expressed in a common currency.
Key Characteristics of PPP:
- Standardized Comparison: Compares currencies based on their purchasing power instead of nominal exchange rates.
- Adjustment for Cost of Living: Accounts for differences in living costs across countries.
- Used for International Economic Comparisons: Helps in comparing GDP, wages, and overall economic productivity.
- Long-Term Stability: Less volatile than market exchange rates, providing a stable measure of economic strength.
How is PPP Calculated?
The Purchasing Power Parity Exchange Rate is determined by comparing the price of a standard basket of goods and services in two countries.
PPP Formula:
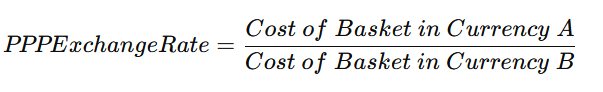
For example, if a basket of goods costs ₹1,000 in India and $20 in the US, the PPP exchange rate would be:

This means that, under PPP, 1 USD should ideally be equal to 50 INR based on purchasing power.
Types of PPP
1. Absolute PPP:
Suggests that the price of an identical basket of goods should be the same in two countries when expressed in a common currency.
Formula:
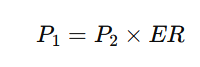
Where:
P₁ = Price of the basket in Country 1
P₂ = Price of the basket in Country 2
ER = Exchange rate between the two countries
2. Relative PPP:
States that the change in exchange rates between two currencies over time should be proportional to the difference in their inflation rates.
Formula:
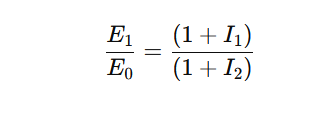
E₁ = Future exchange rate
E₀ = Current exchange rate
I₁ = Inflation rate in Country 1
I₂ = Inflation rate in Country 2
Importance of PPP in Economics
1. Comparing Economic Strength:
PPP-adjusted GDP provides a more accurate comparison of economic output between countries by adjusting for differences in living costs.
2. Exchange Rate Determination:
PPP helps economists and policymakers determine whether a currency is overvalued or undervalued compared to another.
3. Cost of Living Adjustments:
International organizations use PPP to measure global poverty and set fair wage comparisons across nations.
4. Investment Decisions:
Businesses use PPP to assess market potential and pricing strategies when expanding into foreign markets.
PPP vs. Market Exchange Rates
| Feature | PPP Exchange Rate | Market Exchange Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Basis of Calculation | Cost of identical goods | Supply and demand in forex markets |
| Stability | More stable | Highly volatile |
| Reflects Cost of Living? | Yes | No |
| Used For | Long-term economic comparisons | Short-term trading, forex markets |
| Affected By | Inflation differences | Speculation, trade flows |
Challenges in Using PPP
1. Variation in Goods and Services:
- Goods and services differ across countries, making it difficult to create a truly identical basket.
2. Transportation and Trade Barriers:
- Tariffs, shipping costs, and regulations can distort the actual cost of goods.
3. Quality Differences:
- Even if goods are similar, quality variations can affect price comparisons.
4. Exchange Rate Fluctuations:
- Market exchange rates often differ significantly from PPP values due to speculative trading and global economic conditions.
Real-World Applications of PPP
1. The Big Mac Index:
- Created by The Economist, this index compares the price of a McDonald’s Big Mac in different countries to estimate PPP exchange rates.
2. IMF and World Bank Reports:
- PPP is used to compare GDP and living standards across nations, helping in policy formulation.
3. Global Business Strategy:
- Companies use PPP to adjust pricing models and understand market affordability.
4. International Wage Comparisons:
- Economists use PPP to compare minimum wages and labor costs globally.
Conclusion
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) is a fundamental concept in international economics, offering a more accurate way to compare economic strength and living standards across countries. While it has limitations due to trade barriers, quality differences, and exchange rate fluctuations, it remains a crucial tool for policymakers, businesses, and researchers. By adjusting for cost-of-living differences, PPP ensures fairer economic comparisons and better decision-making in global trade, investment, and policy formulation.


Pingback: Comparing Liquid Funds and Liquid ETFs: Which is Right for You? - Bharat Articles
Pingback: Understanding Demat Debit and Pledge Instruction (DDPI) - Bharat Articles
Pingback: Growth Option vs IDCW - Which One to Choose While Investing?
Pingback: CDSL Easiest: Features, Benefits, and Registration Process