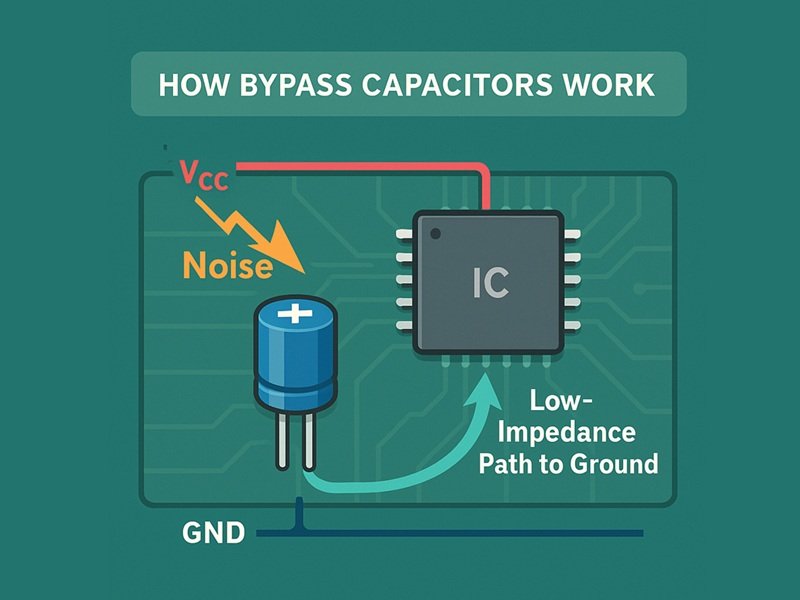
How Do Bypass Capacitors Work
How Bypass Capacitors Work
Bypass capacitors operate on their ability to store and release electrical charge in an improved fashion. At the time of instantaneous current demand within the circuit, bypass capacitors are able to deliver energy far quicker than main power sources. This rapid response maintains a stable voltage level and prevents low voltage situations that could hamper circuit performance.
Bypass capacitors act as low-impedance paths for high-frequency signals and short unwanted signals to ground, thereby preventing interference with the proper operation of sensitive components. This noise-filtering action is crucial in digital circuits, where clean power supplies are essential for accurate signal processing.
Applications of Bypass Capacitors
Mixed-signal systems
Mixed-signal systems contain both analog and digital components and, therefore, largely on bypass capacitors for the integrity of signals. These capacitors are effective in decoupling the analog and digital portions of a circuit, shielding sensitive analog signals from the onslaught of digital noise. This is especially crucial where data converters (ADCs and DACs) are concerned, as noise would heavily compromise purity and the associated accuracy of conversion.
Power supply decoupling
Among pernicious applications of bypass capacitors is power supply decoupling, placing these components near the power inputs of ICs and other components. This minimizes ripple on the power supply voltage and provides a stable power supply. This is even more critical for complex systems with multiple voltage domains or inclusion of switching power supplies capable of generating some noise.
RF and high-frequency circuits
Bypass capacitors are employed in RF and high-frequency circuits for the sake of maintaining signal integrity and minimizing unwanted coupling between different stages of a circuit. Bypass capacitors help to provide a low-impedance path to ground for high-frequency noise thereby reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and boosting general circuit performance. This is even more applicable to wireless communication systems in which signal quality is necessary for maintaining high data rates and long-range of communication.
Proper Installation and Placement
Optimal positioning on PCB
When installing bypass capacitors, optimal positioning on the PCB is crucial for effective noise suppression. These capacitors should be as close to the power pins of the IC they support as possible. The smaller the loop area between the capacitor and IC, the less parasitic inductance involved and thus the better the high-frequency performance.
Minimizing lead length
The length of the traces connecting the bypass capacitor to the IC’s power and ground pins should be kept as short as possible. Longer leads introduce unwanted inductance, which can diminish the capacitor’s effectiveness at higher frequencies. Use wide, short traces to minimize resistance and inductance, ensuring the capacitor can respond quickly to sudden current demands.
Grounding considerations
Proper grounding is essential for bypass capacitors to function effectively. Connect the capacitor’s ground terminal directly to the ground plane using a via placed as close to the capacitor as possible. This technique reduces the ground return path impedance, enhancing the capacitor’s ability to shunt high-frequency noise to ground.

Read This Also: HDI PCB Trends in 2026: Innovations and Challenges
Troubleshooting with Bypass Capacitors
Identifying noise-related issues
In troubleshooting sets of electronic circuits, noise-related issues manifest as unwanted fluctuation in voltage or current. Such disruptions can be harmful to the circuit performance-if not produce system failure. Hence, when dealing with noise-related problems, keep your sights peeled for intermittent operation, unexpected signal distortions, or unexplained voltage drops. Use an oscilloscope to visualize the noise on power supply lines or sensitive signal paths. Pay close attention to high-frequency oscillations or sudden spikes that could indicate inadequate bypass capacitor performance.
Testing and measuring capacitor performance
To check the bypass capacitor performance, some special test equipment would be required, like an impedance analyzer or LCR meter. Such equipment would measure various properties, including the actual capacitance value, equivalent series resistance (ESR), and resonant frequency. Any discrepancies between the measurements and the manufacturer’s specifications need to be checked. A high-frequency oscilloscope can test the capacitor’s ability to filter transients and to keep the DC voltage stable while in operation. Look for minimal voltage ripple and quick response to load changes as indicators of proper bypass capacitor function.
Replacing faulty bypass capacitors
Once the defective bypass capacitor is discovered, it must be replaced with a substitute or better working. The substitute capacitor must, at the least, have an equivalent capacitance, voltage rating, and temperature characteristics. The new capacitor should be soldered in place with very short leads, with the respect to polarity, for better filtering performance. After changing the capacitor, the circuit should be gone through to see if it performs better with less noise. It is especially important to mention that this sometimes works: using capacitors of better quality or connections of two or more capacitors in parallel benefits from improved noise suppression and added stability to the whole system.