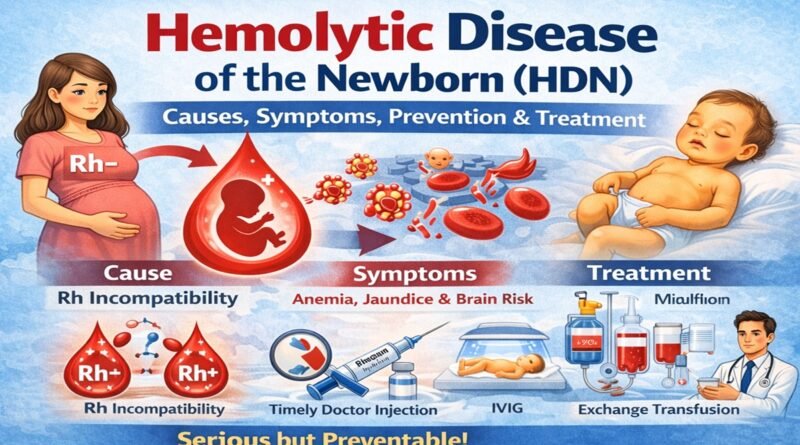
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN): Causes, Symptoms, Prevention & Treatment (Complete Guide)
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN) is a condition in which a baby’s red blood cells are destroyed by the mother’s immune system during pregnancy or after birth.
Medically called:
👉 Hemolytic disease of the newborn
It used to be a major cause of newborn deaths decades ago — but today, with modern medicine, it is largely preventable and treatable.
What Happens in HDN?
Normally, the mother’s immune system protects the body from foreign cells.
But sometimes during pregnancy:
- Baby’s blood enters mother’s circulation
- Mother’s body thinks baby blood is “foreign”
- Antibodies are produced
- These antibodies destroy baby’s red blood cells
This leads to anemia and jaundice in the baby.
Main Cause: Rh Incompatibility
The most common reason is
👉 Rh incompatibility
Risk Condition
- Mother → Rh negative (−)
- Father → Rh positive (+)
- Baby → Rh positive (+)
Now mother produces antibodies against baby’s blood.
Why First Pregnancy is Usually Safe
During first pregnancy:
- Mother has not yet formed antibodies
During delivery:
- Blood mixing occurs
- Antibodies develop
Second pregnancy becomes high-risk
Other Causes (Not Only Rh)
HDN can also happen due to ABO mismatch:
Mother O → Baby A or B
Also rare antigen systems:
- Kell
- Duffy
- Kidd
These sometimes cause even more severe disease than Rh.
Read this: Rare Blood Groups: Types, Genetics, Availability & Medical Importance (Complete Guide)
Symptoms in the Baby
Before Birth (Ultrasound Findings)
- Swelling (hydrops fetalis)
- Enlarged liver
- Fluid in abdomen
- Placenta enlargement
After Birth
- Severe jaundice within 24 hours
- Pale skin
- Rapid breathing
- Weak cry
- Enlarged spleen
Why It Is Dangerous
Destroyed RBCs release bilirubin.
High bilirubin can damage brain → kernicterus (permanent brain injury).
So early treatment is critical.
Diagnosis
Doctors check:
Mother Tests
- Blood group typing
- Antibody screening
- Indirect Coombs test
Baby Tests
- Direct Coombs test
- Bilirubin levels
- Hemoglobin levels
Prevention (Most Important Part)
Doctors prevent HDN using an injection:
👉 Rho(D) immune globulin
When Given
- 28 weeks pregnancy
- Within 72 hours after delivery
- After miscarriage / abortion
- After bleeding during pregnancy
This injection stops antibody formation.
Prevention success rate: over 99%
Treatment After Birth
Depends on severity.
Mild
- Phototherapy (blue light treatment)
Moderate
- IV immunoglobulin (IVIG)
Severe
- Exchange transfusion (replace baby’s blood)
Prognosis
With modern treatment:
- Most babies recover fully
- Brain damage is preventable
- Mortality now extremely low
Early detection is key.
Myths vs Facts
| Myth | Truth |
|---|---|
| Rh negative women cannot have children | False |
| All pregnancies at risk | Only specific cases |
| Disease unavoidable | Completely preventable |
| Baby always affected | Rare with treatment |
Final Conclusion
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn is a serious but preventable condition.
Key takeaways:
- Caused by blood incompatibility
- Usually affects second pregnancy
- Prevented by timely injection
- Treatable if detected early
Today, no baby should suffer from HDN if proper antenatal care is taken.