Blood Groups Explained: Types, Genetics, Pregnancy, Compatibility & Medical Importance (Complete Guide)
Blood group is one of the most important biological identities of a human body.
It affects blood transfusion, pregnancy, organ donation, immunity, and emergency medicine.
Yet many people only know their blood type as A, B, O or AB — without understanding what it actually means.
This article explains everything about blood groups in simple language.
1. What is a Blood Group?
A blood group is determined by special proteins and sugars present on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs).
These markers are called antigens.
Your immune system recognizes these antigens and decides:
- Accept (same type)
- Attack (different type)
If wrong blood enters the body → immune system destroys it → dangerous reaction.
2. The Two Main Blood Group Systems
Human blood type is decided by two systems:
(A) ABO System
Types:
- A
- B
- AB
- O
This system was discovered by
👉 Karl Landsteiner
who later received the Nobel Prize.
(B) Rh System
Determined by presence or absence of
👉 Rh factor
If present → Positive (+)
If absent → Negative (−)
Example:
A+, B−, O+, AB−
Read this also: Husband–Wife Blood Group & Rh Factor: Does It Affect Pregnancy?
3. How ABO Blood Groups Work
| Blood Group | Antigen on RBC | Antibody in Plasma |
|---|---|---|
| A | A antigen | Anti-B |
| B | B antigen | Anti-A |
| AB | A and B | None |
| O | None | Anti-A & Anti-B |
Why this matters
If a person receives incompatible blood → antibodies attack RBC → clotting → kidney failure → death.
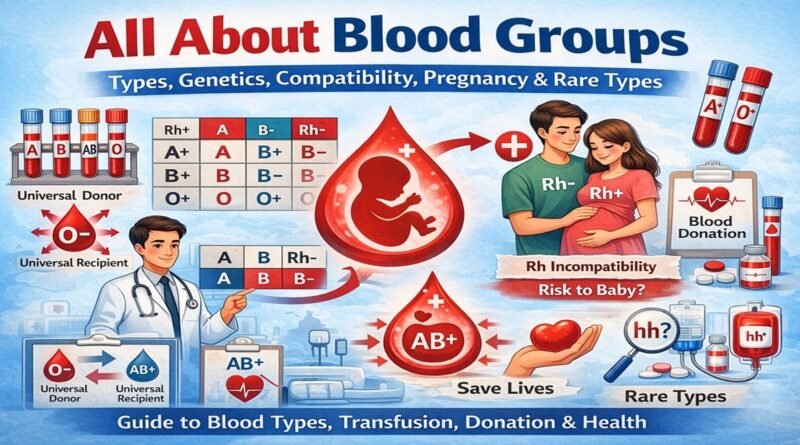
4. Blood Transfusion Compatibility
Who can receive from whom?
| Recipient | Can Receive From |
|---|---|
| O | O only |
| A | A, O |
| B | B, O |
| AB | A, B, AB, O (Universal Receiver) |
Universal Donor
O negative (O−) → emergency lifesaver
Universal Recipient
AB positive (AB+)
5. Rh Factor & Pregnancy
Most important real-life medical relevance.
Problem occurs only when:
Mother Rh − and Baby Rh +
This is called
👉 Rh incompatibility
It can cause
👉 Hemolytic disease of the newborn
What happens?
Mother’s immune system attacks baby’s RBCs:
- Jaundice
- Anemia
- Swelling
- Rare severe complications
Modern prevention
Doctors give
👉 Rho(D) immune globulin
This prevents antibody formation and makes pregnancy safe.
Today this condition is fully manageable.
6. Genetics: How Baby’s Blood Group is Determined
Blood group comes from parents via genes.
ABO inheritance
| Parents | Possible Child |
|---|---|
| A + A | A, O |
| A + B | A, B, AB, O |
| O + O | O only |
| AB + O | A, B |
Rh inheritance
Rh+ is dominant, Rh− recessive.
- Rh+ parent may carry hidden negative gene
- Rh− parent always gives negative gene
So baby can be positive even if one parent is negative.
7. Blood Groups & Health (Scientific Observations)
Research shows associations:
| Blood Type | Higher Risk |
|---|---|
| A | Gastric cancer |
| O | Ulcers but lower heart disease |
| AB | Memory disorders |
| B | Diabetes tendency |
(These are statistical tendencies, not certainties.)
8. Blood Groups & Immunity
Blood group antigens also exist in:
- Saliva
- Digestive tract
- Respiratory tract
They affect:
- Infection susceptibility
- Gut bacteria
- Viral attachment
Example: Some viruses attach better to certain blood groups.
9. Rare Blood Groups
Some extremely rare types exist:
- Bombay Blood Group (hh phenotype)
- Rh null (Golden Blood)
These require specially matched donors worldwide.
10. Blood Donation Importance
A single donation can save 3 lives:
- Trauma patient
- Surgery
- Newborn
O− donors are especially valuable in emergencies.
11. Myths vs Facts
| Myth | Truth |
|---|---|
| Couples need matching blood group | False |
| Different blood groups cause infertility | False |
| Rh negative pregnancy dangerous | Preventable |
| Blood group decides personality | No scientific proof |
Final Conclusion
Blood group is medically crucial but socially misunderstood.
Key points:
- Blood group does NOT affect marriage compatibility
- Matters mainly in transfusion and pregnancy
- Rh incompatibility is preventable
- Knowing your blood group can save lives
The most important step:
Always know and record your blood type.