ISRO Rockets: A Comprehensive Overview of India’s Space Launch Vehicles
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has been at the forefront of space exploration, contributing significantly to global advancements in space technology. Since its inception in 1969, ISRO has developed a range of launch vehicles to place satellites into orbit and conduct space missions. This article provides a detailed analysis of ISRO’s rockets, highlighting their development, capabilities, and impact on India’s space missions.
Historical Development of ISRO’s Launch Vehicles
The Beginnings: SLV and ASLV
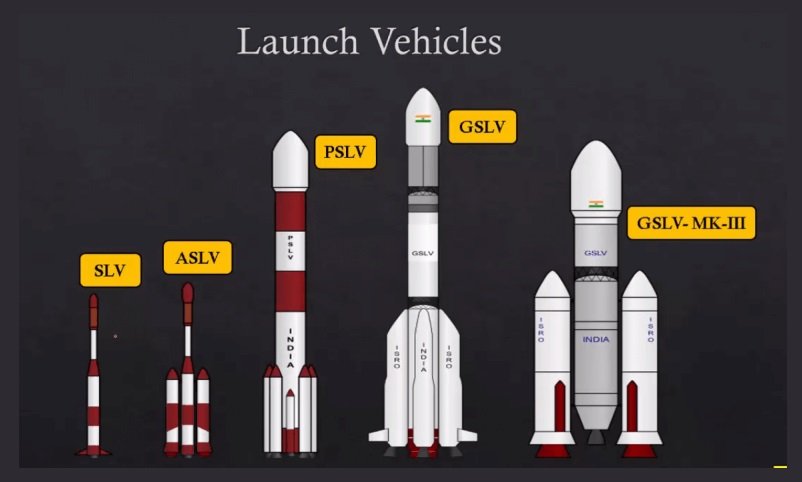
Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV):
- First Launch: 1980
- Details: The SLV was India’s first experimental satellite launch vehicle. It successfully placed the Rohini satellite into low Earth orbit (LEO) in July 1980. This achievement marked India as the sixth country to demonstrate satellite launch capability.
- Specifications: The SLV was a four-stage solid propellant rocket with a payload capacity of 40 kg.
Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV):
- First Launch: 1987
- Details: The ASLV was developed to enhance payload capacity and reliability. It faced initial failures but eventually succeeded in placing satellites into orbit.
- Specifications: It had a five-stage solid propellant configuration with a payload capacity of 150 kg to LEO.
The Workhorses: PSLV and GSLV
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV):
- First Launch: 1993
- Details: PSLV is one of the most successful and versatile launch vehicles developed by ISRO. It is capable of placing satellites into polar, geosynchronous, and sun-synchronous orbits.
- Specifications: It is a four-stage rocket with a combination of solid and liquid propellants, capable of carrying payloads up to 1,750 kg to sun-synchronous orbit (SSO) and 3,800 kg to LEO.
- Notable Missions: PSLV has launched numerous satellites, including India’s Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) and the Chandrayaan-1 mission to the Moon. It also set a world record by launching 104 satellites in a single mission in February 2017 (IDRW) .
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV):
- First Launch: 2001
- Details: GSLV is designed to launch heavier payloads into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO). The development of GSLV included the incorporation of an indigenously developed cryogenic upper stage.
- Specifications: It is a three-stage rocket with solid, liquid, and cryogenic stages, capable of carrying payloads up to 2,500 kg to GTO.
- Notable Missions: GSLV has been crucial for launching communication satellites like GSAT series, and the launch of Chandrayaan-2, India’s second lunar exploration mission (IDRW) .
Advanced Launch Vehicles: GSLV Mk III and SSLV
GSLV Mk III (LVM-3):
- First Launch: 2014 (experimental), 2017 (operational)
- Details: GSLV Mk III, also known as LVM-3, is ISRO’s most powerful launch vehicle to date. It is designed for launching heavier payloads and is intended to support India’s human spaceflight program.
- Specifications: It is a three-stage vehicle with two solid rocket boosters (S200), a liquid core stage (L110), and a cryogenic upper stage (C25). It can carry up to 4,000 kg to GTO and 10,000 kg to LEO.
- Notable Missions: GSLV Mk III successfully launched the GSAT-19 and GSAT-29 satellites. It is also designated to launch the Gaganyaan mission, India’s first crewed spaceflight program .
Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV):
- First Launch: Upcoming
- Details: SSLV is designed to meet the growing demand for launching small satellites. It aims to provide on-demand launch services with a shorter turnaround time and lower costs.
- Specifications: SSLV is a three-stage solid propellant vehicle with a payload capacity of 500 kg to LEO and 300 kg to SSO.
- Notable Missions: SSLV’s first mission will focus on launching small commercial satellites, aiming to cater to the global small satellite market (IDRW) .
Technological Innovations and Achievements
Indigenous Development
ISRO has made significant strides in developing indigenous technologies for its launch vehicles. The successful development of cryogenic engines, which are crucial for heavy-lift capabilities, is a testament to India’s growing prowess in space technology. The indigenous development of the semi-cryogenic engine and advancements in composite materials for rocket stages further highlight ISRO’s commitment to self-reliance.
Reusability and Cost Efficiency
ISRO is actively working on reusable launch vehicle technology to reduce the cost of access to space. The Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD) program aims to develop technologies that can be integrated into future reusable launch vehicles. This initiative aligns with global trends towards more sustainable and cost-effective space missions.
International Collaboration
ISRO’s launch vehicles have been instrumental in launching satellites for various countries, fostering international collaboration in space. The PSLV, in particular, has earned a reputation as a reliable and cost-effective launcher, attracting commercial satellite launch contracts from around the world.
Impact on India’s Space Program
Advancing Scientific Research
ISRO’s rockets have enabled numerous scientific missions, contributing to our understanding of space and planetary sciences. Missions like Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan have placed India among the select group of nations capable of interplanetary exploration.
Boosting Communication and Connectivity
The successful deployment of communication satellites using GSLV and PSLV has significantly improved telecommunications, broadcasting, and internet services in India. This has had a profound impact on the socio-economic development of the country.
Enhancing National Security
ISRO’s launch capabilities have also strengthened India’s national security. The deployment of earth observation and reconnaissance satellites has enhanced India’s surveillance and monitoring capabilities, crucial for national defense and disaster management.
Future Prospects
Human Spaceflight Program
The Gaganyaan mission, set to launch astronauts into space, is a major milestone for ISRO. The GSLV Mk III will play a pivotal role in this mission, marking India’s entry into human space exploration.
Deep Space Missions
ISRO has ambitious plans for deep space exploration, including missions to study the Sun (Aditya-L1), Venus, and further lunar and Mars missions. These missions will leverage the capabilities of ISRO’s advanced launch vehicles, pushing the boundaries of space exploration.
Commercial Launch Services
With the development of SSLV and advancements in reusable launch technologies, ISRO aims to capture a significant share of the global small satellite launch market. This will position India as a key player in the commercial space sector, offering competitive and reliable launch services.
Conclusion
ISRO’s journey from the humble beginnings of SLV to the advanced GSLV Mk III has been marked by significant achievements and technological innovations. The development and success of these rockets have not only bolstered India’s space capabilities but also positioned ISRO as a major player in the global space arena. As ISRO continues to push the envelope with new missions and technological advancements, the future of India’s space program looks brighter than ever.
For further details, you can visit the Indian Space Research Organisation