Gross Domestic Product (GDP): A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is one of the most important indicators used to measure the economic performance of a country. It represents the total value of all final goods and services produced within a nation’s borders over a specific period, usually a quarter or a year. Policymakers, economists, and investors rely on GDP to assess economic growth and make informed decisions.
What is GDP?
Definition:
GDP is the monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country in a given time frame. It serves as a key measure of economic activity and helps compare the economic performance of different countries.
Key Characteristics of GDP:
- Comprehensive Measure: Includes all economic activities within a country’s borders.
- Final Goods Focus: Avoids double counting by considering only finished products.
- Time-Bound Calculation: Measured on a quarterly or annual basis.
- Indicator of Economic Health: A rising GDP suggests economic growth, while a declining GDP may indicate recession.
Methods of Calculating GDP
There are three primary methods to calculate GDP, each providing a different perspective on economic activity:
1. Production Method
Also known as the Value-Added Method.
Measures GDP by calculating the total value added at each stage of production.
Formula:
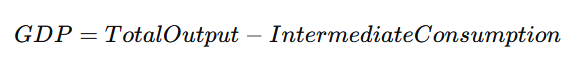
2. Income Method
Measures GDP by summing all incomes earned in an economy, including wages, profits, rent, and taxes.
Formula:
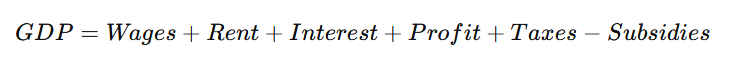
3. Expenditure Method
Measures GDP by summing total spending on goods and services in an economy.
Formula:

Types of GDP
1. Nominal GDP
- Measures GDP at current market prices without adjusting for inflation.
- Useful for year-to-year comparisons but can be misleading due to price fluctuations.
2. Real GDP
Adjusted for inflation to reflect the true growth of an economy.
Formula:
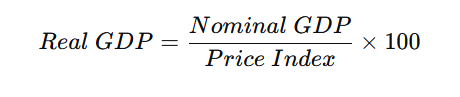
3. GDP Per Capita
Measures GDP per person, offering insights into the average economic output per citizen.
Formula:
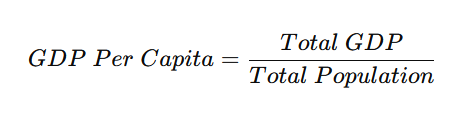
4. Gross National Product (GNP) vs. GDP
GDP measures production within a country’s borders, while GNP includes income from abroad.
Formula:
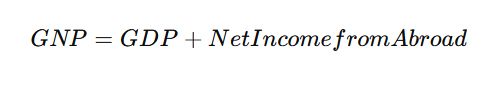
Importance of GDP
1. Economic Growth Indicator:
- A rising GDP signifies a growing economy, attracting investment and job creation.
2. Policy Making:
- Governments use GDP data to design economic policies, including taxation and spending.
3. Global Comparisons:
- GDP helps compare economic performance across countries, influencing trade and foreign investment.
4. Standard of Living Measurement:
- GDP per capita provides insights into the living standards of a nation’s population.
Challenges in GDP Measurement
1. Exclusion of Informal Economy:
- Many developing countries have large informal sectors that are not fully accounted for in GDP.
2. Inflation Effects:
- Nominal GDP figures can be misleading without adjusting for inflation.
3. Environmental and Social Factors Ignored:
- GDP does not account for environmental degradation or income inequality.
4. Data Accuracy:
- Dependence on statistical agencies can lead to discrepancies and revisions.
Conclusion
GDP remains the most widely used economic indicator for assessing national and global economic performance. However, while it provides a useful snapshot of economic activity, it has limitations in capturing overall well-being and sustainability. To make well-rounded economic decisions, GDP should be analyzed alongside other indicators like GNP, HDI, and employment rates.

