Concept of Base Year in Financial and Economic Analysis
Understanding the Concept of Base Year in Financial and Economic Analysis
The base year is a fundamental concept in economics, finance, and statistics, serving as a reference point for comparing data across different time periods. It is used to measure economic performance, inflation, and stock market indices by providing a standardized benchmark. This helps in evaluating changes in various economic indicators over time.
What is a Base Year?
A base year is a specific year chosen as a benchmark for comparing economic or financial data across different periods. It is assigned a fixed value, often set at 100 in index calculations, against which future values are compared. The base year helps in tracking growth trends and inflation-adjusted changes in prices, output, and other economic parameters.
Key Characteristics of a Base Year:
- Fixed Reference Point: It acts as a standard against which changes in variables like GDP, price indices, and stock market indices are measured.
- Standardized Value: Generally, the base year is assigned an index value of 100 for ease of calculation.
- Regular Updates: The base year is revised periodically to reflect more recent economic conditions and maintain relevance.
Importance of a Base Year
The selection of a base year is crucial in various financial and economic analyses. Here’s why:
- Economic Growth Measurement:
- Used to compare Gross Domestic Product (GDP) over different years, helping policymakers understand economic progress.
- Inflation Calculation:
- Helps compute the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Wholesale Price Index (WPI), which indicate inflation trends.
- Stock Market Indices:
- Used in index calculations such as Nifty 50, Sensex, and Nifty Midcap 150, where the base year provides a reference for market performance.
- Comparative Analysis:
- Aids investors, economists, and policymakers in making data-driven decisions based on historical comparisons.
How is a Base Year Selected?
The selection of a base year depends on several factors:
- Stability: The year chosen should represent normal economic conditions, avoiding periods of extreme volatility or crisis.
- Recent and Relevant Data: It should be periodically updated to reflect current economic realities.
- Comparability: Should allow for easy comparison of past and future economic data.
- Government and Statistical Agencies: National statistical agencies such as the Central Statistics Office (CSO) in India decide on the base year for various economic indicators.
Examples of Base Years in Different Economic Indicators:
| Indicator | Base Year |
|---|---|
| GDP Calculation (India) | 2011-12 (Current) |
| Consumer Price Index (CPI) | 2012 |
| Wholesale Price Index (WPI) | 2011-12 |
| Nifty 50 Index | 1995 |
| Sensex Index | 1978-79 |
Base Year in Stock Market Indices
Stock market indices like Nifty 50, Nifty Midcap 150, and Sensex use a base year to track market performance over time. The index value is calculated as:
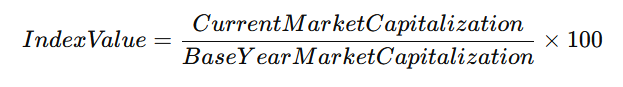
This formula allows investors to assess stock market trends compared to the base year.
Example:
- If the Sensex base year (1978-79) was assigned a value of 100, and today’s value is 50,000, it indicates significant market growth over time.
Revising the Base Year
Governments and statistical agencies periodically revise the base year to maintain relevance in economic assessments. The revision process involves:
- Collecting New Data: Updating price levels, output, and financial data to reflect modern economic conditions.
- Re-evaluating Sectoral Composition: Adjusting economic sectors to include emerging industries.
- Ensuring Better Representation: Incorporating a wider data set for more accurate analysis.
Example: India revised its GDP base year from 2004-05 to 2011-12 to improve data accuracy and better reflect contemporary economic activities.
Challenges in Selecting a Base Year
While the base year concept is useful, there are some challenges:
- Frequent Updates Required: Economic conditions change over time, requiring regular updates.
- Data Discrepancies: Different methodologies in data collection can lead to inconsistencies.
- Impact of Unforeseen Events: Events like financial crises, pandemics, or technological disruptions can distort the base year’s effectiveness.
- Comparability Issues: Changing the base year can lead to differences in historical comparisons, sometimes causing confusion.
Conclusion
The base year is a vital tool in economic and financial analysis, serving as a reference for comparing various indices, market trends, and macroeconomic indicators. It ensures consistency, accuracy, and meaningful comparisons over time. Whether in GDP calculations, inflation measurement, or stock market indices, the base year provides a foundation for assessing economic progress and financial performance.
Regular updates to the base year help maintain its relevance, ensuring it accurately reflects modern economic conditions. Investors, policymakers, and analysts must consider the base year’s role when interpreting financial and economic data for better decision-making.
Disclaimer: This blog has been written exclusively for educational purposes. The securities mentioned are only examples and not recommendations. This does not constitute a personal recommendation/investment advice. It does not aim to influence any individual or entity to make investment decisions. Recipients should conduct their own research and assessments to form an independent opinion about investment decisions.

