What is Carbon Farming?
What is Carbon Farming?
Carbon farming is a sustainable agricultural practice that focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and increasing carbon sequestration in the soil. It involves implementing various farming techniques and land management practices that help to capture and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thus mitigating climate change.
Why is Carbon Farming Important?
Carbon farming plays an imp role in combating climate change and promoting environmental sustainability. By adopting carbon farming practices, farmers can contribute to reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and improve the health of their soils. This not only helps to mitigate climate change but also enhances the resilience of agricultural systems and promotes biodiversity.
The Process of Carbon Farming
Carbon farming involves several key processes that work together to enhance carbon sequestration and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Let’s take a closer look at these processes:
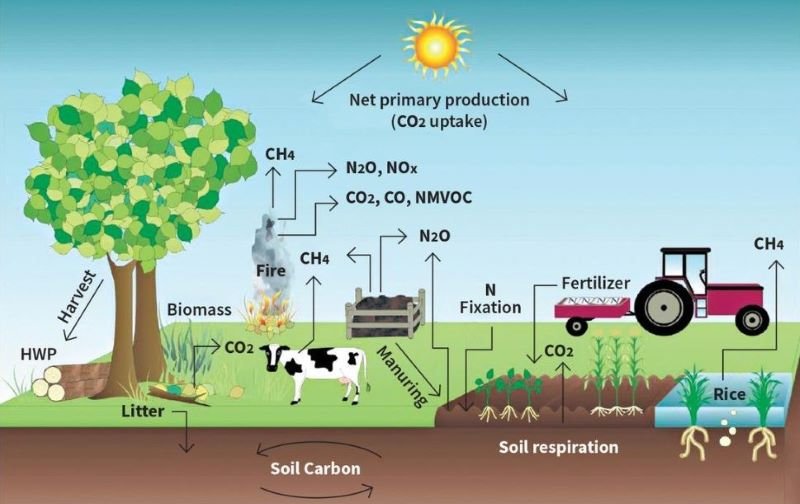
1. Regenerative Agriculture
Regenerative agriculture is a fundamental aspect of carbon farming. It focuses on building healthy soil ecosystems that can absorb and store carbon dioxide. This is achieved through practices such as cover cropping, crop rotation and minimal tillage. These techniques help improve soil health, increase organic matter content and enhance the soil’s ability to sequester carbon.
2. Agroforestry
Agroforestry is another important component of carbon farming. It involves integrating trees into agricultural landscapes, providing multiple benefits such as carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation and improved soil fertility. Trees capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass and in the soil, making agroforestry a powerful tool for climate change mitigation.
3. Conservation Tillage
Conservation tillage is a practice that minimizes soil disturbance during planting and cultivation. By reducing or eliminating tillage, farmers can prevent the release of carbon dioxide stored in the soil and reduce fuel consumption. Conservation tillage also helps improve soil structure, water infiltration and overall soil health.
4. Nutrient Management
Effective nutrient management is crucial in carbon farming. By optimizing fertilizer application and utilizing organic amendments, farmers can minimize nitrogen losses and reduce nitrous oxide emissions. Nitrous oxide is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Implementing precision agriculture techniques can also help ensure that nutrients are applied efficiently, reducing waste and environmental impact.
5. Livestock Management
Livestock management plays a significant role in carbon farming. Sustainable grazing practices, such as rotational grazing and managed intensive grazing, can help improve soil health and increase carbon sequestration. These practices involve moving livestock regularly to different areas, allowing for proper rest and recovery of pastures. By avoiding overgrazing and implementing proper manure management, farmers can minimize methane emissions, another potent greenhouse gas.
Opportunities for Carbon Farming in India
India, with its vast agricultural landscape and diverse climatic conditions, presents significant opportunities for carbon farming:
Enhanced Soil Health and Fertility
Carbon farming practices such as composting, organic farming, and conservation agriculture can improve soil health and fertility. This, in turn, enhances crop productivity and resilience to climate change impacts.
Water Conservation
Implementing carbon farming practices like agroforestry and contour plowing can help conserve water and reduce irrigation requirements. This is particularly important in water-stressed regions of India where sustainable water management is crucial for agriculture.
Climate Change Mitigation
By sequestering carbon in the soil, carbon farming can contribute to climate change mitigation efforts. India, being one of the largest greenhouse gas emitters, can significantly reduce its carbon footprint through widespread adoption of carbon farming practices.
Rural Livelihoods and Income Diversification
Carbon farming practices can offer additional income streams for farmers through carbon credit trading and ecosystem service payments. This can help improve rural livelihoods and reduce dependence on traditional agricultural practices.
Biodiversity Conservation
Many carbon farming practices, such as agroforestry and habitat restoration, promote biodiversity conservation. By creating diverse ecosystems, carbon farming contributes to the preservation of native flora and fauna, enhancing overall ecological resilience.
Benefits of Carbon Farming
1. Climate Change Mitigation: Carbon farming practices help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by sequestering carbon in the soil. By capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, these practices help to mitigate climate change and contribute to global efforts to reduce carbon emissions.
2. Improved Soil Health: Carbon farming techniques, such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and conservation tillage, promote the health of the soil. These practices increase organic matter content, enhance soil fertility, improve water retention, and reduce erosion. Healthy soils are more resilient to climate change impacts, such as droughts and floods, and support the growth of healthy crops.
3. Biodiversity Conservation: Carbon farming practices often involve the restoration of native vegetation, creation of wildlife habitats, and conservation of natural resources. These activities contribute to the conservation of biodiversity by providing shelter, food, and breeding grounds for various plant and animal species.
4. Economic Benefits: Carbon farming can provide economic benefits to farmers through the sale of carbon credits or participating in carbon offset programs. These initiatives incentivize farmers to adopt sustainable practices and provide an additional source of income.
Carbon Farming Practices
There are several carbon farming practices that farmers can adopt to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase carbon sequestration:
1. Conservation Tillage: This practice involves reducing or eliminating tillage to minimize soil disturbance and carbon loss. By leaving crop residues on the soil surface, conservation tillage helps to increase organic matter content and improve soil structure.
2. Cover Cropping: Cover crops, such as legumes or grasses, are planted between main crops to protect the soil from erosion, suppress weeds, and improve soil fertility. They also capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in the soil.
3. Agroforestry: Agroforestry combines the cultivation of trees or shrubs with agricultural crops or livestock. Trees sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, provide shade, enhance biodiversity, and improve soil health.
4. Nutrient Management: Proper management of fertilizers and manure can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural activities. By optimizing nutrient application and using organic fertilizers, farmers can minimize nitrogen losses and improve soil nutrient availability.
5. Wetland Restoration: Wetlands are highly effective in sequestering carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. Restoring and preserving wetlands on agricultural lands can significantly contribute to carbon sequestration and provide additional benefits, such as water filtration and wildlife habitat.
Challenges to Carbon Farming
While carbon farming offers numerous benefits, there are several challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption:
Lack of Awareness and Education
One of the major challenges is the limited awareness and understanding of carbon farming practices among farmers. Many farmers are unaware of the potential benefits and the techniques involved in carbon farming. Therefore, there is a need for educational programs and training initiatives to bridge this knowledge gap.
Financial Constraints
Implementing carbon farming practices often requires investments in infrastructure, equipment, and training. Small-scale farmers, in particular, may face financial constraints in adopting these practices. Access to affordable financing options and government support can help overcome this challenge.
Technical Expertise
Carbon farming involves implementing specific techniques such as agroforestry, cover cropping, and rotational grazing. Farmers may require technical expertise and guidance to implement these practices effectively. Providing access to agronomic experts and extension services can help farmers overcome this challenge.
Policy and Regulatory Framework
There is a need for supportive policy frameworks and regulations that incentivize carbon farming practices. Clear guidelines, financial incentives, and market-based mechanisms can encourage farmers to adopt sustainable farming practices that promote carbon sequestration.
The Future of Carbon Farming
As the world faces the challenges of climate change, carbon farming is gaining recognition as a valuable solution. Governments, organizations, and farmers are increasingly adopting carbon farming practices to reduce emissions and enhance sustainability. The future of carbon farming lies in scaling up these practices and integrating them into mainstream agriculture.
Research and innovation are also contributing to the development of new carbon farming techniques and technologies. This includes advancements in precision agriculture, remote sensing, and soil carbon measurement tools. These innovations will further enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of carbon farming practices.
By embracing carbon farming, we can create a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system while actively combating climate change. It is a win-win solution that benefits the environment, farmers, and future generations.
