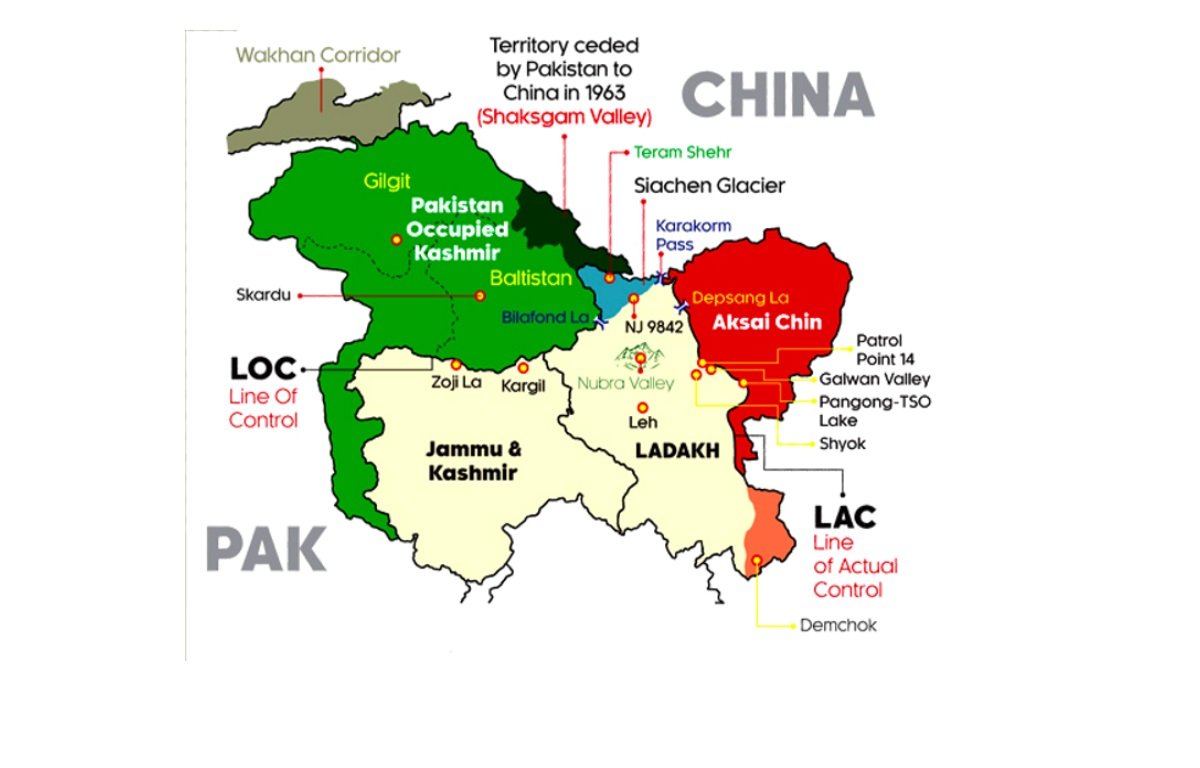
Understanding the Shaksgam Valley Dispute of India with China and Pak
The Shaksgam Valley, also known as the Trans-Karakoram Tract, is a region nestled in the northernmost part of the disputed territory of Jammu and Kashmir. This valley has been a subject of contention between India, Pakistan, and China for many years. In this article, we will delve into the history, significance, and current status of the Shaksgam Valley, focusing on China’s occupation of the region.
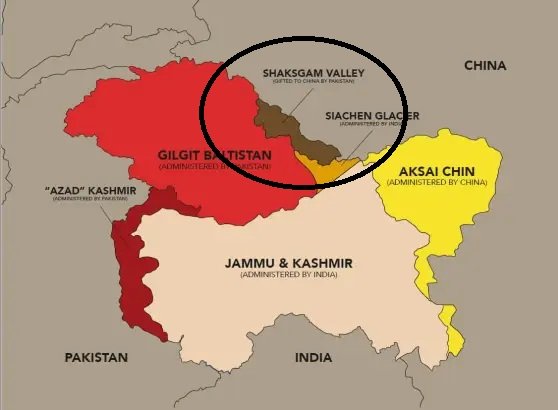
A Historical Perspective
The Shaksgam Valley has a rich historical background, with its origins dating back to the ancient Silk Road trade route. It has been a strategically important region due to its location connecting Central Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East. The valley was historically part of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, which was under the rule of the Dogra dynasty.
Following the partition of India in 1947, the princely states were given the choice to accede to either India or Pakistan. However, the Shaksgam Valley was not included in the Instrument of Accession signed by the Maharaja of Jammu and Kashmir with India. Instead, it was leased by Pakistan to China in 1963, under a controversial agreement known as the Sino-Pakistan Boundary Agreement.
The Sino-Pakistan Boundary Agreement
The Sino-Pakistan Boundary Agreement, signed on March 2, 1963, formalized the transfer of the Shaksgam Valley from Pakistan to China. Under this agreement, Pakistan ceded around 5,180 square kilometers of territory to China, including the Shaksgam Valley. In return, China recognized Pakistan’s sovereignty over the remaining portion of Jammu and Kashmir.
The agreement was met with widespread criticism, particularly from India, which considered the transfer of territory as a violation of its own territorial integrity. India claims the entire region of Jammu and Kashmir, including the Shaksgam Valley, as an integral part of its territory.
China’s Occupation and Strategic Importance
China’s occupation of the Shaksgam Valley holds significant strategic importance. The valley provides China with a direct land route to Pakistan, bypassing the narrow and vulnerable Wakhan Corridor that separates Afghanistan and Tajikistan. This allows China to establish a more secure connection with its close ally, Pakistan.
Furthermore, the Shaksgam Valley is situated in close proximity to the Siachen Glacier, the world’s highest battleground, which is also a disputed territory between India and Pakistan. China’s presence in the valley gives it an advantageous position to monitor the activities in the region and potentially influence the ongoing conflict between India and Pakistan.
International Response and Implications
The occupation of the Shaksgam Valley by China has drawn international attention and sparked concerns among neighboring countries. India, in particular, has been vocal in its opposition to China’s presence in the region. The Indian government considers the occupation as a direct threat to its territorial integrity and has repeatedly called for the restoration of the valley to its control.
However, China has shown no signs of relinquishing its hold on the Shaksgam Valley. The Chinese government maintains that the region is an integral part of its territory and that the Sino-Pakistan Boundary Agreement is a legally binding agreement. China’s growing influence in the region, both economically and strategically, further complicates the situation.
The occupation of the Shaksgam Valley also has broader implications for the geopolitical landscape in South Asia. It adds another layer of complexity to the already tense relations between India, Pakistan, and China. The region’s strategic importance, coupled with the unresolved territorial disputes, creates a volatile situation that has the potential to escalate tensions in the future.
The Way Forward
Resolving the issue of the Shaksgam Valley’s occupation is a complex task that requires diplomatic efforts from all parties involved. A peaceful resolution would require dialogue and negotiation between India, Pakistan, and China, taking into consideration the concerns and aspirations of all stakeholders.
Conclusion
The Shaksgam Valley’s occupation by China remains a contentious issue in the larger context of the territorial disputes in Jammu and Kashmir. The valley’s strategic importance, coupled with the historical and geopolitical complexities surrounding it, make it a subject of ongoing debate and concern. Resolving the issue will require diplomatic efforts and a genuine commitment to finding a peaceful solution that respects the rights and aspirations of all parties involved.